HowTo Use The NST WUI arp-scan Page To Quickly Locate Hosts
Contents
Overview
The arp-scan command line tool is included with the NST distribution. This is a excellent tool for quickly locating hosts on a network. This utility is well supported and documented. See the Arp-scan User Guide at the NST Open Source Tools Wiki for an excellent write up of what the arp-scan command line utility does.
The NST WUI provides a simple click and run web based interface to the arp-scan command line utility. It is designed to be simple to use and to allow you to further explore the results provided by the arp-scan command line tool.
In addition to helping you identify what systems are connected to your network, this interface can also be helpful in checking your local DNS server as it will try to look up a host name for each IP address found (though this feature can be disabled under the Advanced options).
Locating the "arp-scan" Page In The NST WUI
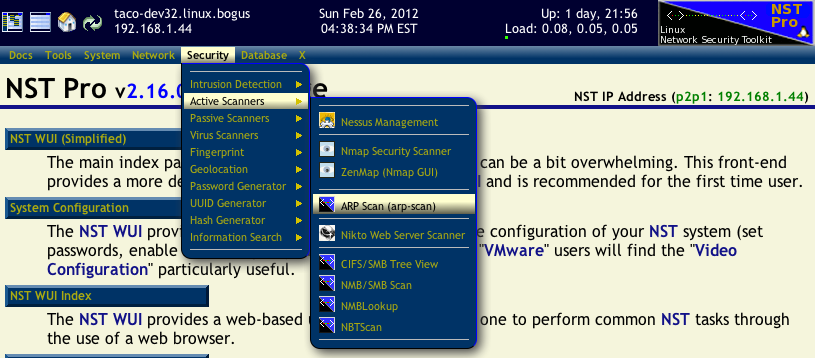
The arp-scan page can be found in the NST WUI using the main menu bar. Select Security -> Active Scanners -> arp-scan as shown in the image below:
Running A Scan
Running a arp-scan is fairly straight forward. Basically, you will:
- Select a network interface to use for the scan.
- Specify a range of IP addresses to scan, or select Local Network if you want to scan every address on the network associated with the interface.
- Optionally open up the Advanced Options area and make some adjustments.
- Press the Run button.
- Wait a few seconds, a few minutes, or hours for the scan to complete. It depends on the address range being scanned as well as various scan options which you can adjust.
- Review the results.
Simple Scan
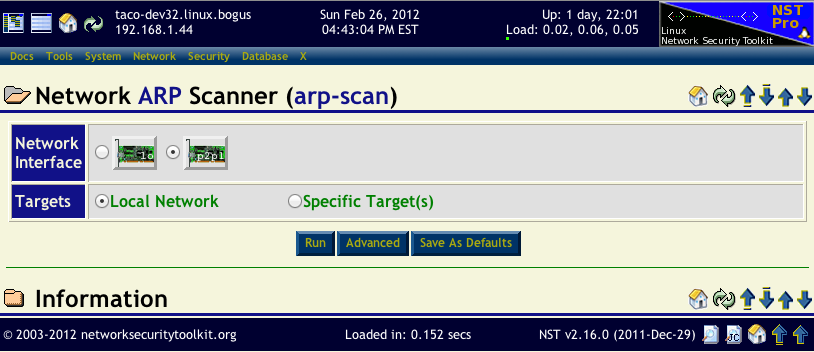
The image below, shows that the p2p1 interface was selected to be scanned and the every host on the p2p1 local network will be scanned. Since it was already known that the p2p1 network in this example was a 192.168.1.0/24 network, we knew it would only take a couple of seconds for the scan to complete. Had the p2p1 been a stealth interface or on a large 10.0.0.0/8 network, we would have specified a specific range of IP addresses to scan.
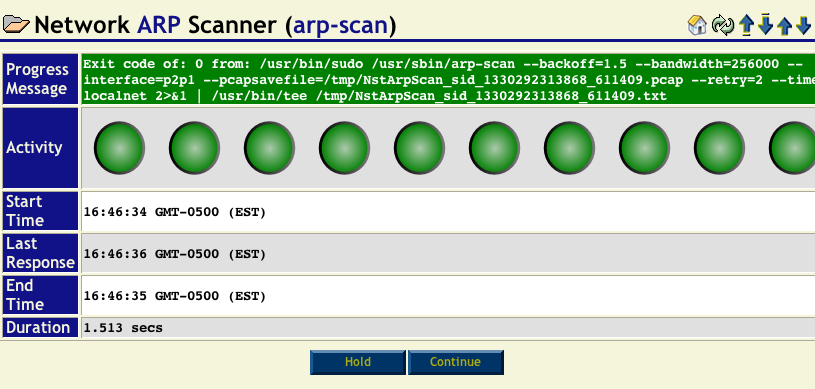
To start the arp-scan the Run button was pressed. The arp-scan progress widget (shown below) was then displayed while the scan went through all of the possible IP addresses.
Once complete, the progress widget will automatically hide itself after a couple of seconds and you will see the final results. If you would like to review the information displayed on the progress widget, press the Hold button before the scan completes.
Reviewing The Results
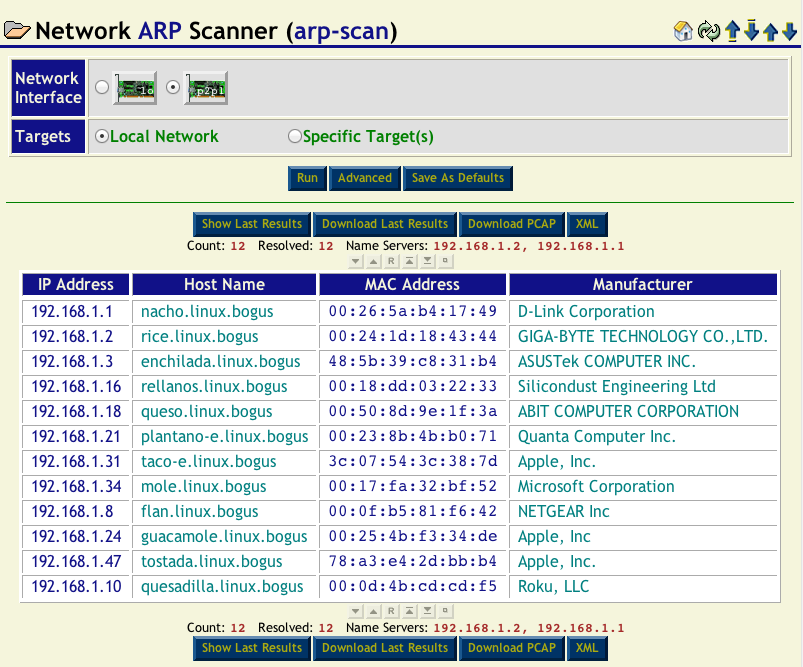
After a arp-scan run completes, you should see a table of IP addresses, host names, MAC addresses and MAC manufacturers similar to what is shown below:
There are many things you can do with the results table:
- You can click on the column headers to sort (or reverse sort) the table by the data contained in the column.
- You can click on any IP address in the table to use other tools in the NST WUI which work with IP addresses.
- You can click on any MAC address in the table to use other tools in the NST WUI which work with MAC addresses.
- You can use the Show Last Results button to see the raw ASCII output from the arp-scan command which was run.
- You can use the Download Last Results button to download the raw ASCII output from the arp-scan command which was run.
- You can use the Download PCAP button to download the PCAP file containing the ARP packets from the scan. This file can be loaded into tools like wireshark.
- You can use the XML button to download a XML file containing the results from the last arp-scan command which was run.
Advanced Options
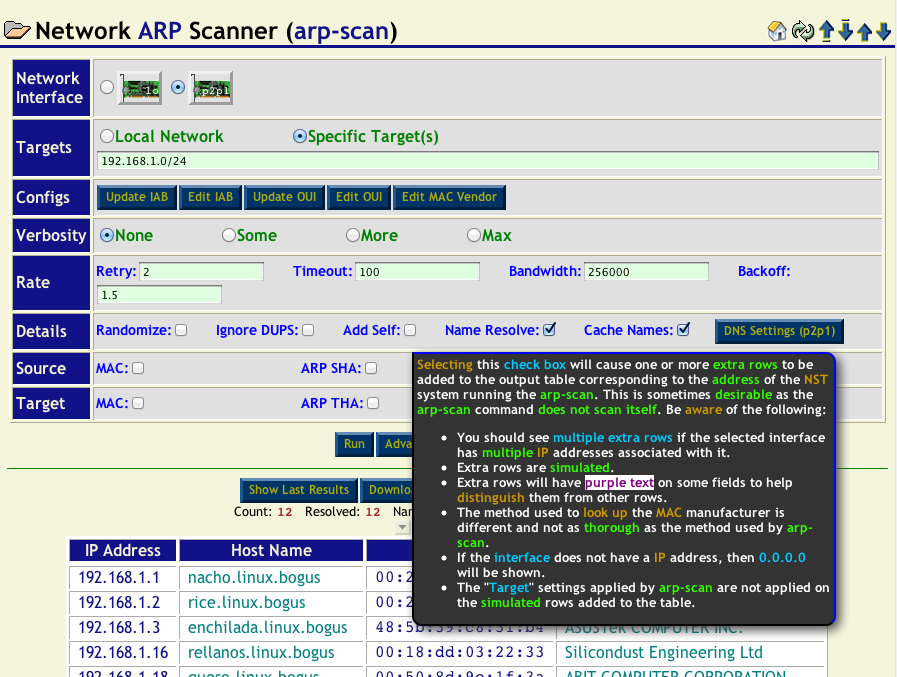
There are many other advanced options which you can specify before running arp-scan. Press the Advanced button to display (or hide if shown) the advanced options. All of the advanced options have tool tips describing what they do. Simply hover your mouse pointer over the option for details. The image below shows the tool tip associated with the Add Self button.
Things To Be Aware Of
Here are some things to be aware of when using this tool:
- It can take a extremely long time to scan a large 10.0.0.0/8 network. We would recommend that you limit your IP address ranges to a 16 bit networks. For example, scanning 10.0.0.0/16, then 10.1.0.0/16, .... Each one of these scans will likely take a few minutes, but trying to scan a 10.0.0.0/8 network will likely take most of the day if you are able to get it to complete at all.
- Do not specify Local Network for stealth interfaces. Since a stealth interface does not have a IP address or network associated with it, specifying Local Network does not make sense.
- The arp-scan utility does not scan itself. So if you would like to see your NST system included in the results table, you must open up the Advanced options and select the Add Self check box. This will add a pseudo entry to the results table.