HowTo Use The NST CloudShark Upload Manager
Overview
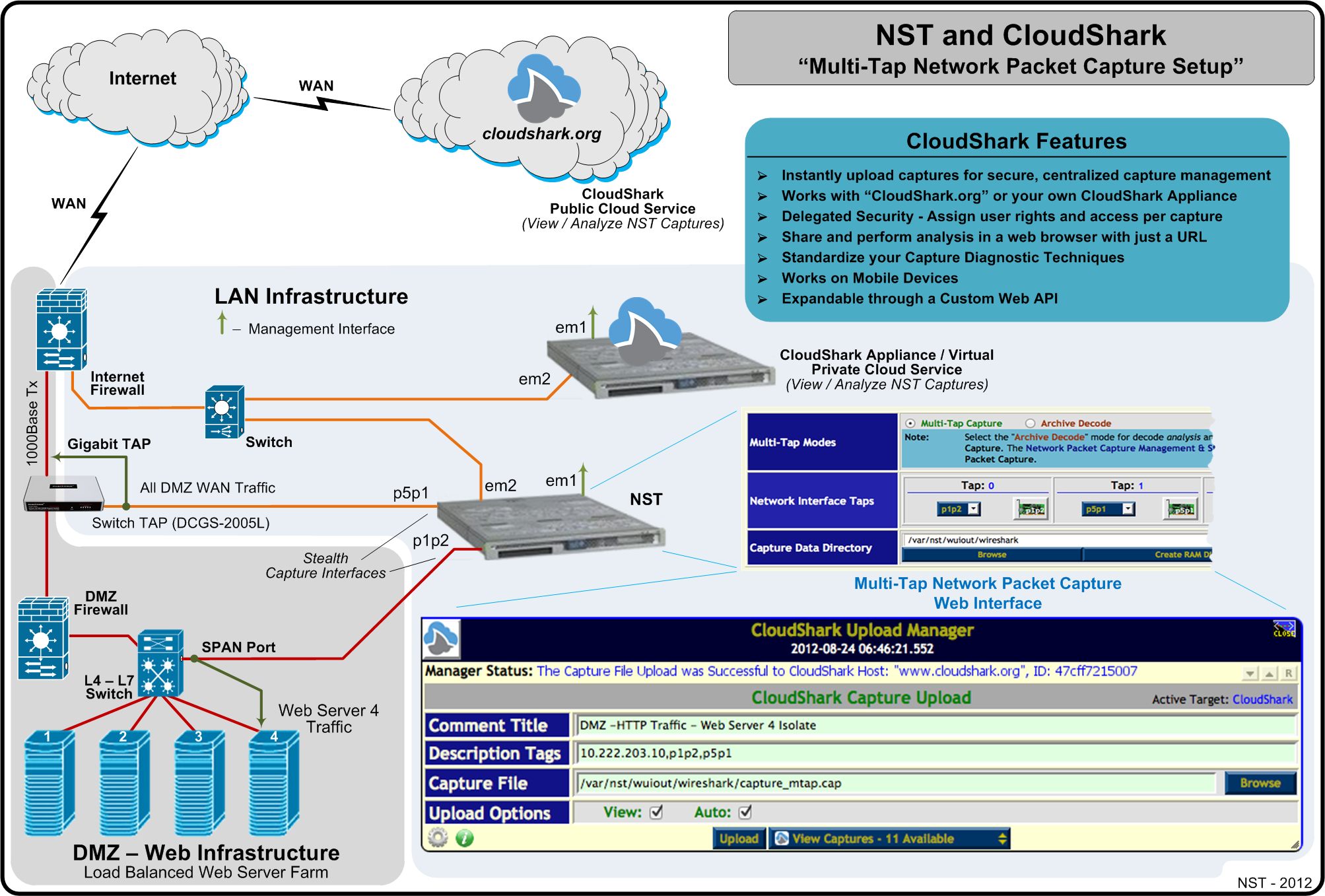
The NST project team has worked with the "CloudShark" folks to facilitate uploading and viewing network packet captures generated by an NST system to either "CloudShark.org" or a "CloudShark Appliance". A new CloudShark Upload Manager tool was created and embedded within the NST WUI to accomplish this. CloudShark technology allows network packet captures generated by an NST system to be imported, viewed, analyzed and shared from anywhere with a Web browser.
NST CloudShark Upload Manager Reference Diagrams

SVN: 4104
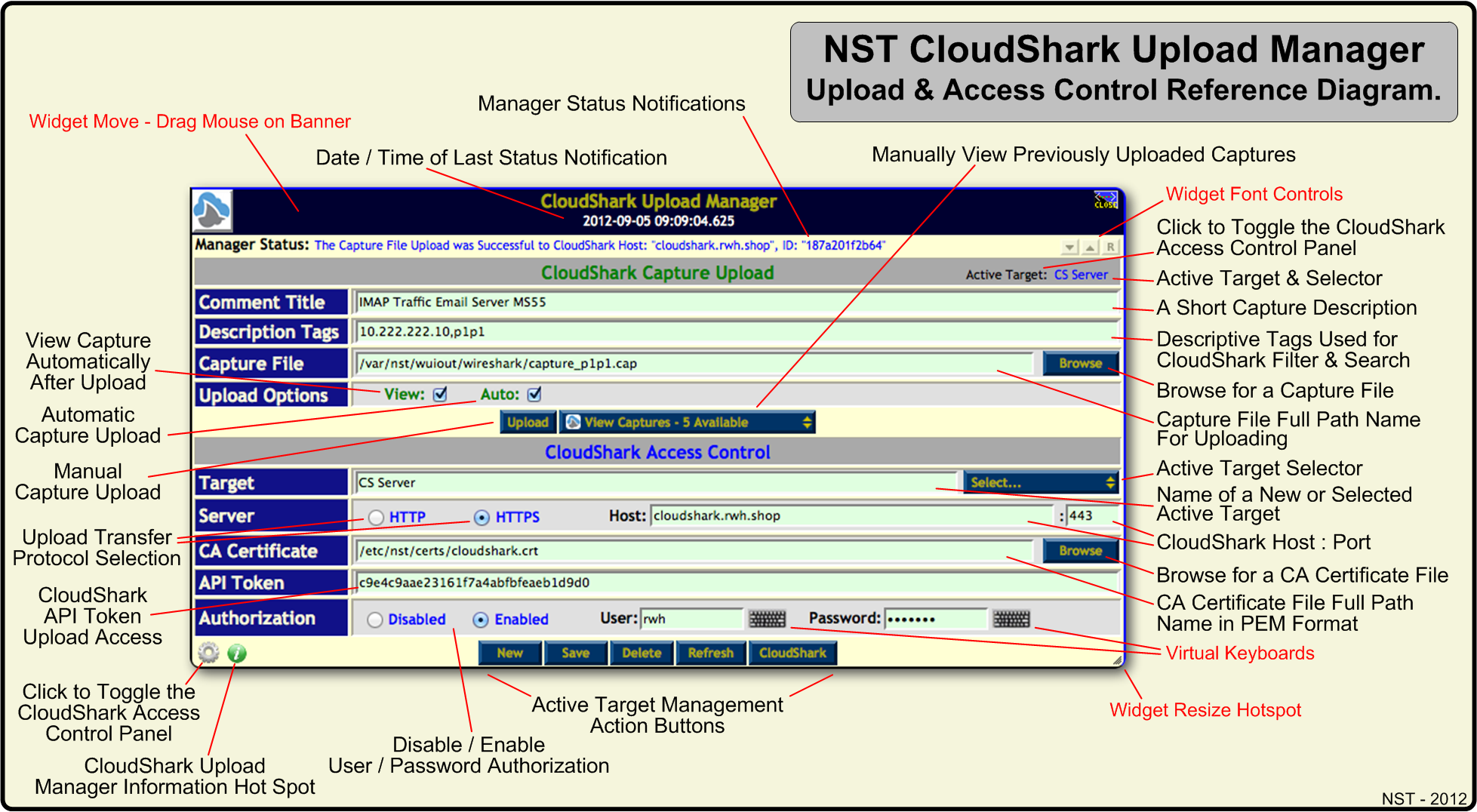
The NST WUI has an integrated "CloudShark Upload Manager" network tools widget for managing the process of transferring a network packet capture to either "CloudShark.org" or a "CloudShark Appliance". The Upload Manager can be configured for either manual or automatic capture uploading and viewing.
One can manually bring up the CloudShark Upload Manager widget through the NST Navigation Menu (i.e. Tools => Network Widgets => CloudShark Upload Manager). All NST WUI pages that can generate a network packet capture can also bring up this widget after a capture has been obtained (i.e., Currently, both the Single and Multi-Tap Network Packet Capture pages as well as the Network ARP Scanner page have this capability.). If the "Automatic Upload Option" is enabled, then the CloudShark Upload Manager's internal transfer process is only used without actually bringing up the widget when uploading a capture from these pages. If the "View Option" is also enabled, then your browser will automatically open up a new tab/window and try to "View" the newly uploaded capture on the associated "CloudShark" host after the a capture has successfully been transferred.
NST CloudShark Upload Manager & Access Control Reference Diagram
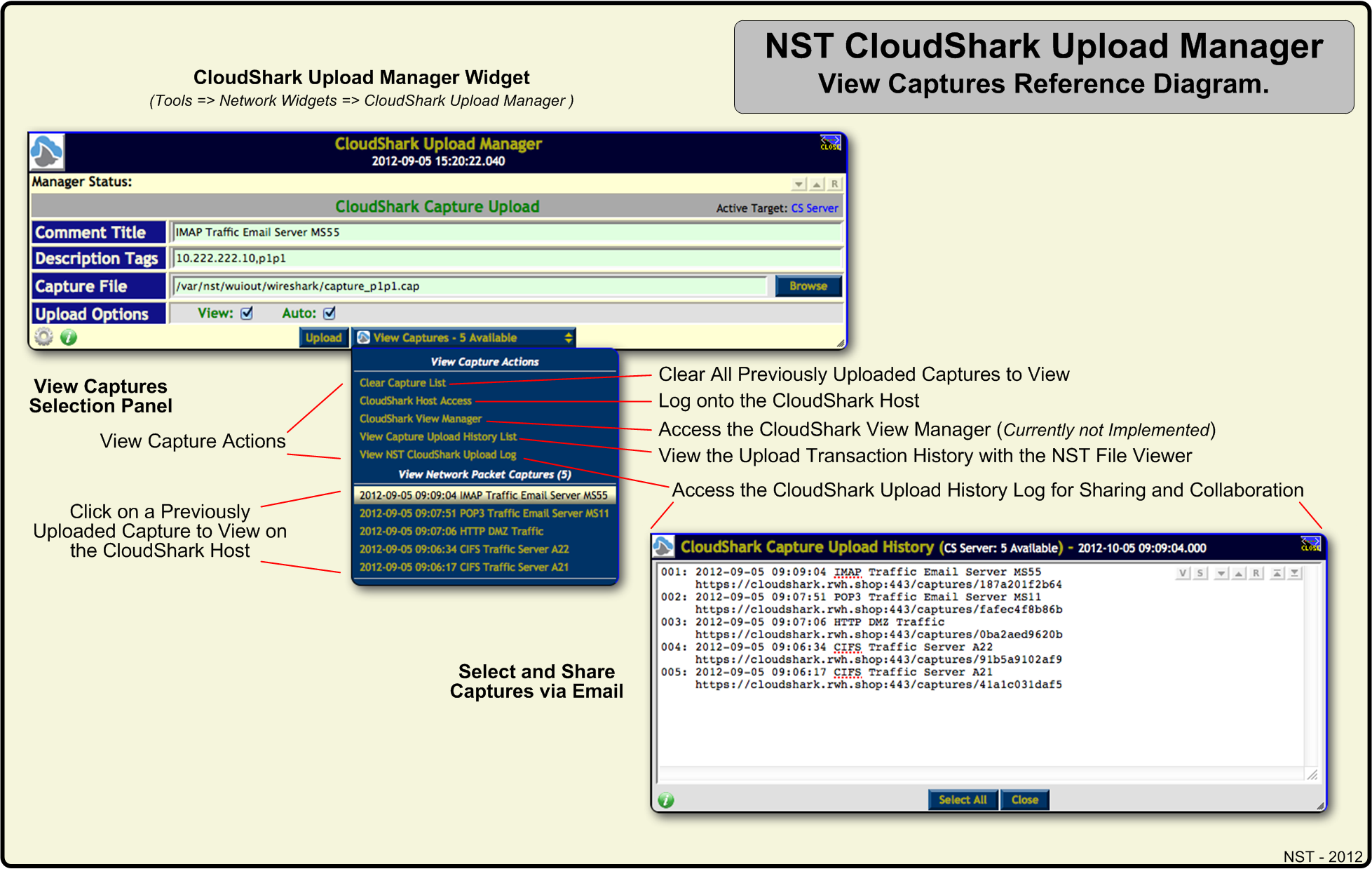
NST CloudShark Upload Manager View Captures Reference Diagram
NST & CloudShark Use Case: Multi-Tap Network Packet Capture Setup
NST & CloudShark Use Case: Single-Tap Network Packet Capture Analysis In A Web Browser
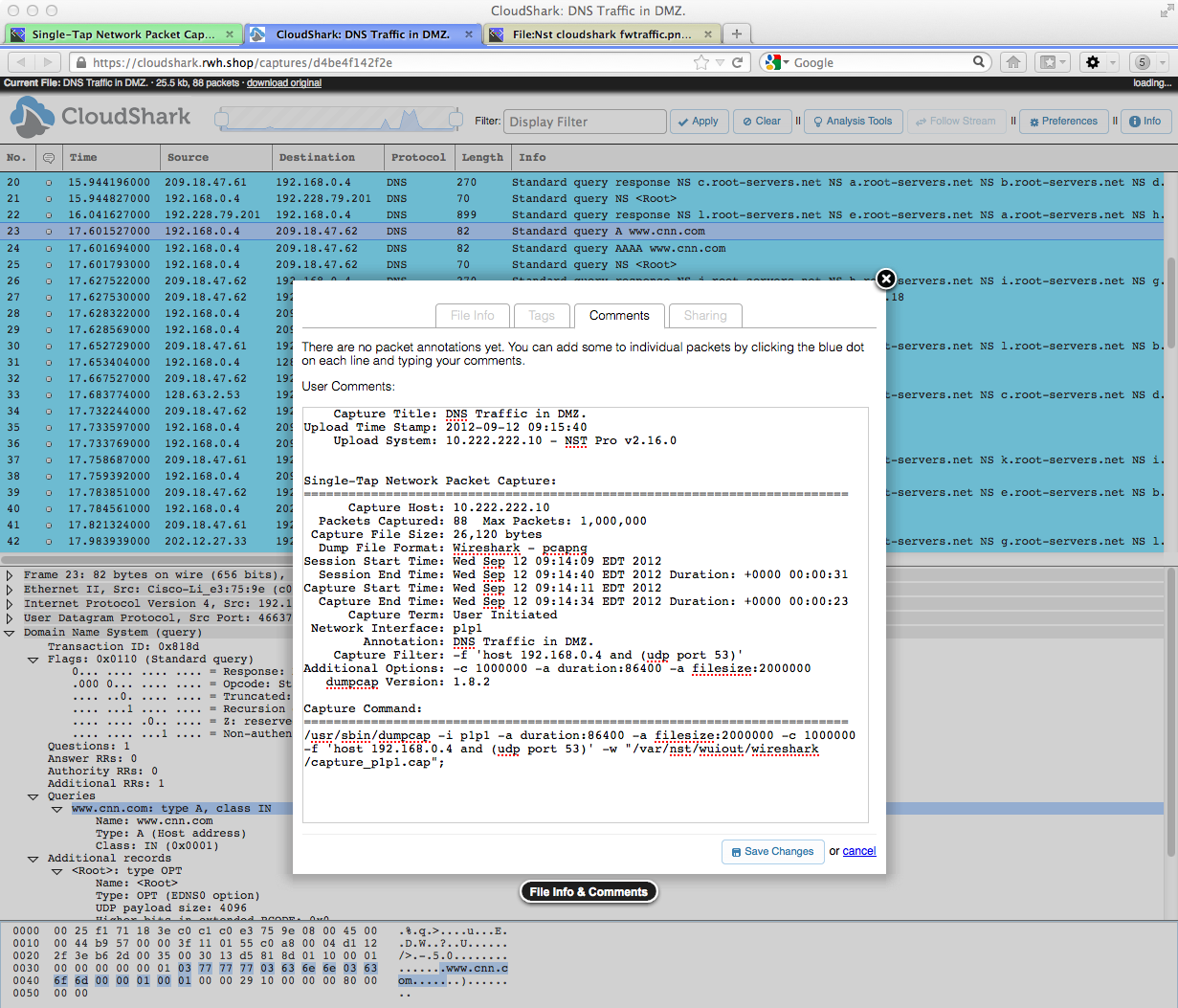
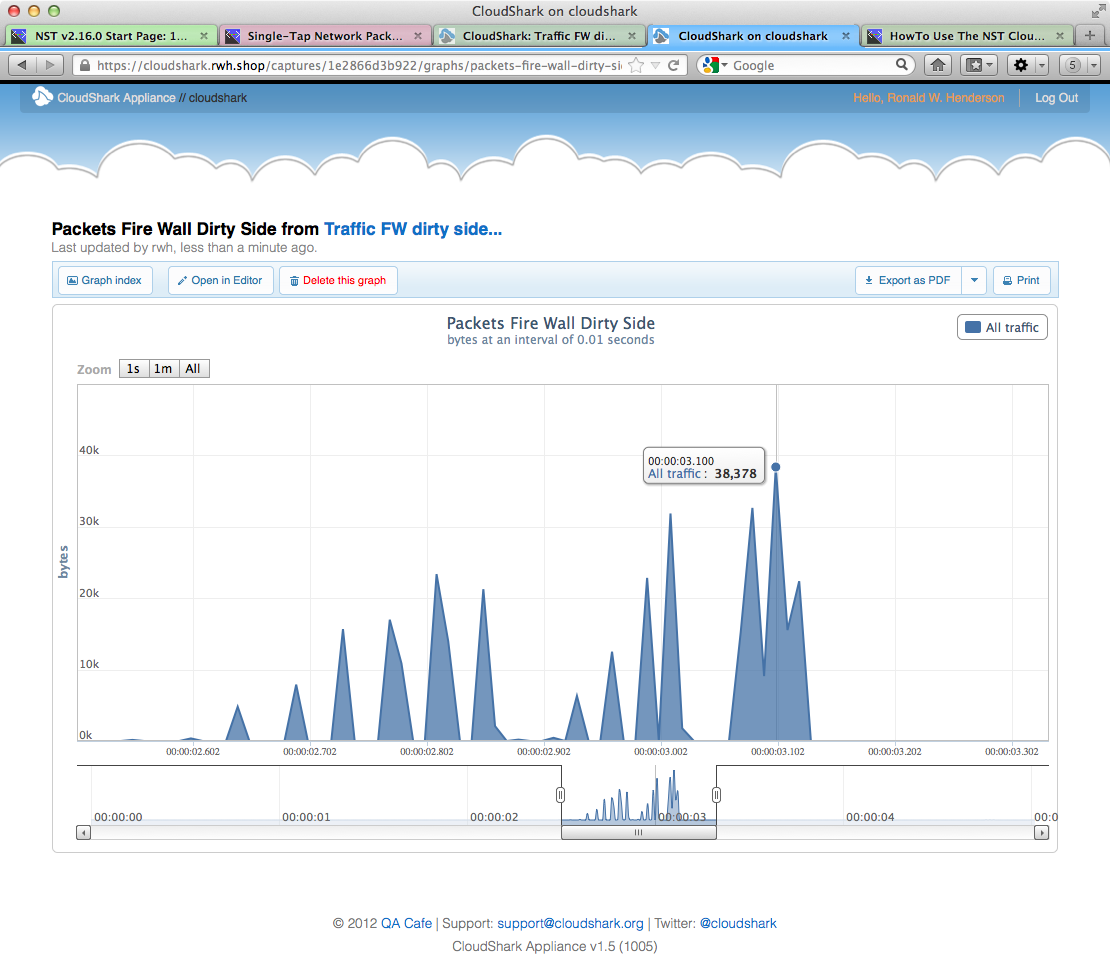
NST & CloudShark Use Case - Graph Analysis: Captured Bytes vs Time