HowTo Setup The NST System To Geolocate Data
Geolocation
We use the term "geolocate", "geolocating" and "geolocation" throughout this page when referring to the process of determining latitude and longitude coordinates associated with an IP address.
Quick Setup
There are many geolocation features available starting with the 2.13.0 release of the NST distribution. Unfortunately, a bit of setup is required in order to make use of these features. The NST WUI provides the "GeoLocation Tools & Management" page in order to simply this setup process.
Locate: "GeoLocation Tools & Management" Page
Once you NST system is booted and running, use a web browser to pull up the NST WUI using the URL of "https://IP_ADDRESS/" where IP_ADDRESS is the IP address of your NST system. Alternatively, if you are on the NST system itself, you can run Firefox and it should automatically pull up the NST WUI for you. When prompted to login, use root and the master password which you previously set using the nstpasswd command.
From the menu bar on the main NST WUI page, select the "GeoLocation Tools & Management" page as shown below:
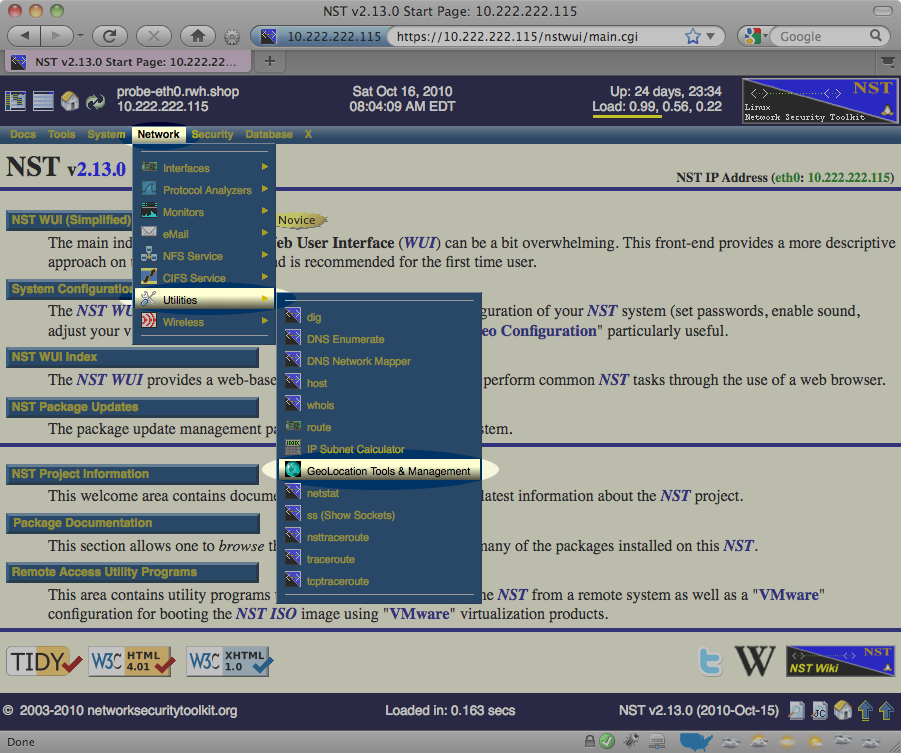
Download Geolocation Databases
Once you've reached the "GeoLocation Tools & Management", scroll down to the "GeoIP Management Options" area, select the Lite City Edition, AS Number Edition checkboxes, the Download radio button and press the Process GeoIP Management Option button as highlighted below:
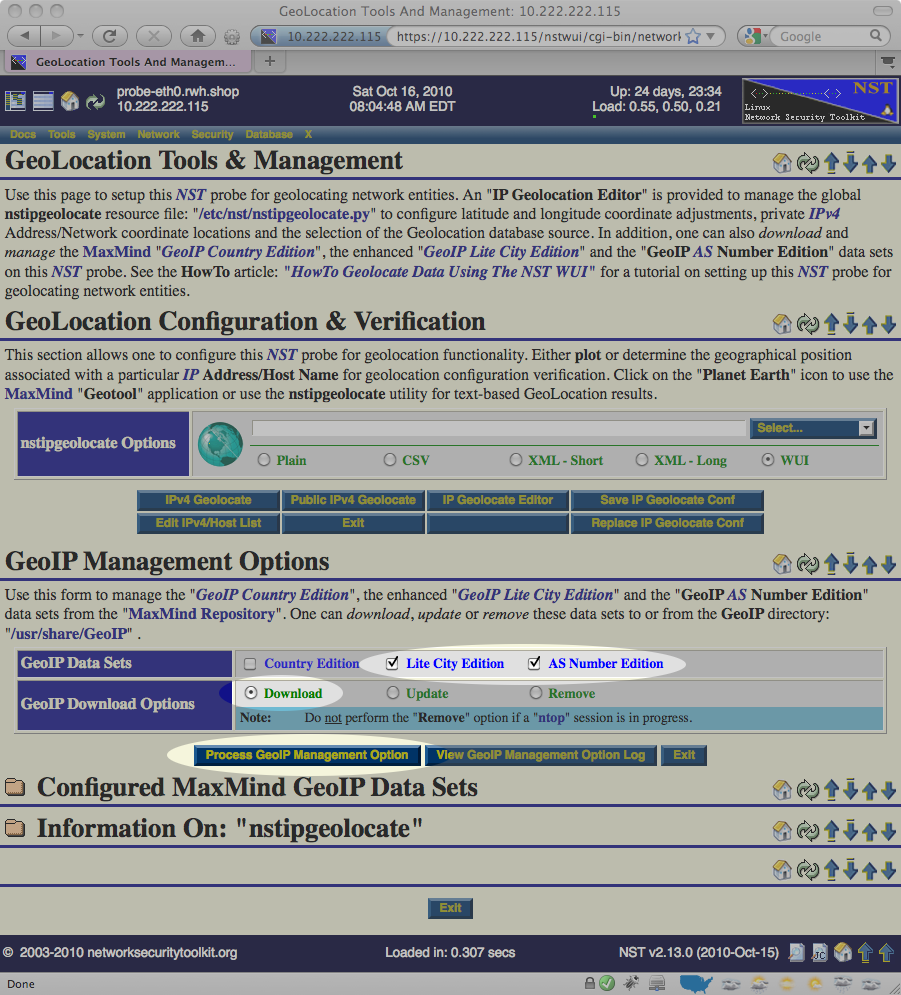
This will take a few moments to complete as the NST will download roughly 40MB of information from the public versions of the databases maintained at http://www.maxmind.com/.
Verify Geolocation is Working
Once the database has been downloaded, you can verify that the NST system is capable of geolocating IP addresses using the same "GeoLocation Tools & Management" page in the NST WUI. To do this:
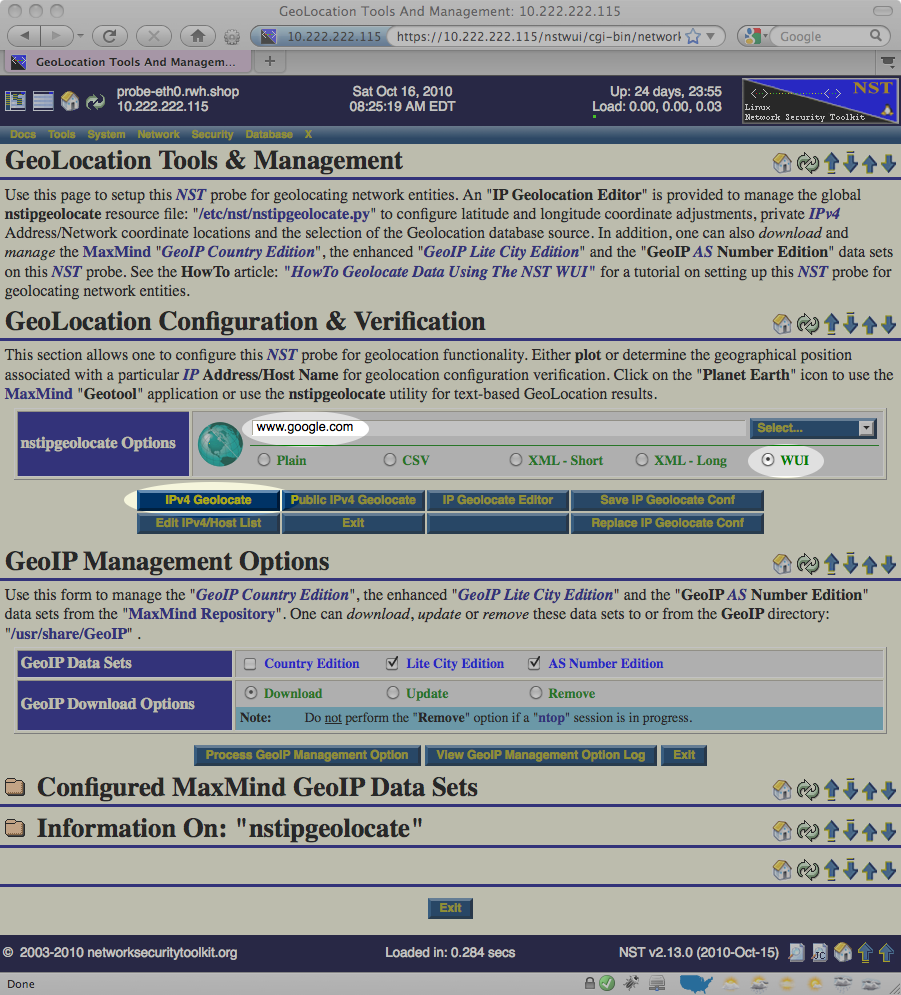
- Locate the GeoLocation IPv4 Addresses / Hosts section near the top of the web page.
- Enter a well known host name or IP address (for example: www.google.com).
- Press the IPv4 GeoLocate button.
The image below demonstrates provides an example of what should be entered:
The image below shows the results displayed after the IPv4 GeoLocate button is pressed:
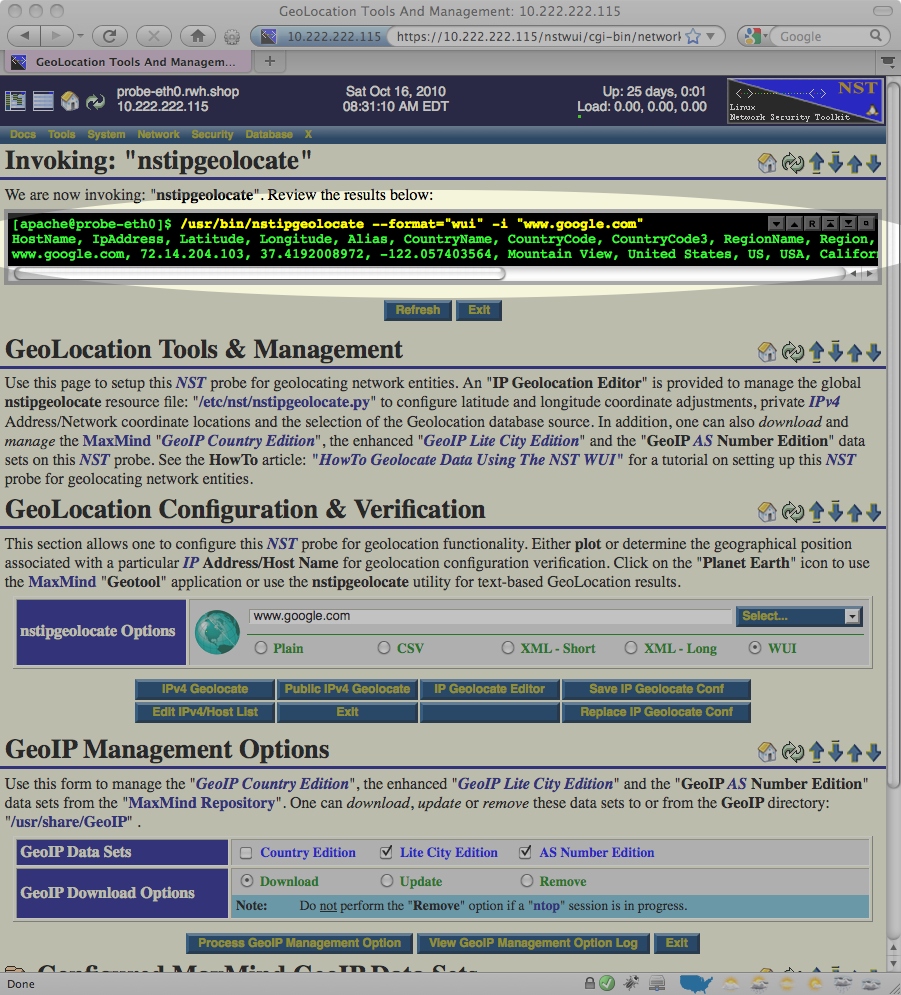
If you look closely in the results output above, you notice that the NST system was able to determine the latitude and longitude coordinates of (37.4192008972, -122.057403564) for www.google.com. This tells us that the NST system has been successfully setup to geolocate public IP addresses.
Advanced Geolocation Setup Notes
MaxMind Download Restrictions
Missing, Incorrect and Private IP Addresses
Missing, Incorrect and Private Networks
Configuration File
The configuration file for the nstipgeolocate command is at: /etc/nst/nstipgeolocate.py. There are many things which can be tweaked in this file.
You must be careful when editing this file as it contains Python code. If you introduce any errors when editing this file it will cause the nstipgeolocate command to fail and your system will no longer be able to geolocate IP addresses. However, you shouldn't be afraid to edit this file as it is heavily commented and provides many template configurations which you should be able to copy/paste/adjust to your liking.
Location Quality
Geolocation Methods
The METHODS parameter in the configuration file is used to list the preferred methods to use and the order to use them in when attempting to geolocate a IP address. The METHODS parameter is specified as a Python string containing one or more of the following available implementations separated by commas:
- ADDR_MAP
- Use the Python hash table defined in the configuration file (look for ADDR_MAP in the configuration file). This is a very quick lookup and allows you to add or correct locations for specific IP addresses.
- NET_MAP
- Use the Python array of networks defined in the configuration file. Each IP address is checked to see if it falls in any of the networks defined in the NET_MAP array (also defined in this configuration file). If found, the location information associated with the network is used.
- GeoIP
- Lookup IP addresses using a local copy of the IP database downloaded from MaxMind. This is a quick operation and is pretty good at locating IP addresses. In addition to the free public database, MaxMind also offers a non-free version of its database. We have not tried this, but we are guessing that if you have access, you should be able to use this database by adjusting the value of the GEOIP_DAT_FILE in the configuration file.
- hostip.info
- Use free web service based geolocation service provided by [1]. This is a relatively slow look up done via HTTP requests. It's not a good choice if you need to geolocate thousands or addresses as we typically see a rate around 15 geolocation lookups per second.
- CATCH_ALL
- Returns a fixed location regardless of IP address passed. If included, it should always be the last entry in the METHODS setting. You can modify this default location by modifying the CATCH_ALL_LOCATION Python tuple that is specified in this file.
For example, the default setting of the METHODS parameter is: "ADDR_MAP,NET_MAP,GeoIP". This means that a NST system will:
- First try to geolocate using the ADDR_MAP implementation.
- If the IP address isn't found, it will next try using the NET_MAP implementation
- If the IP address isn't found, it will next try using the GeoIP implementation.
- If the IP address still isn't found, it will give up (no location found).