HowTo Geolocate kismet Data: Difference between revisions
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
= Kismet Setup and Configuration = | = Kismet Setup and Configuration = | ||
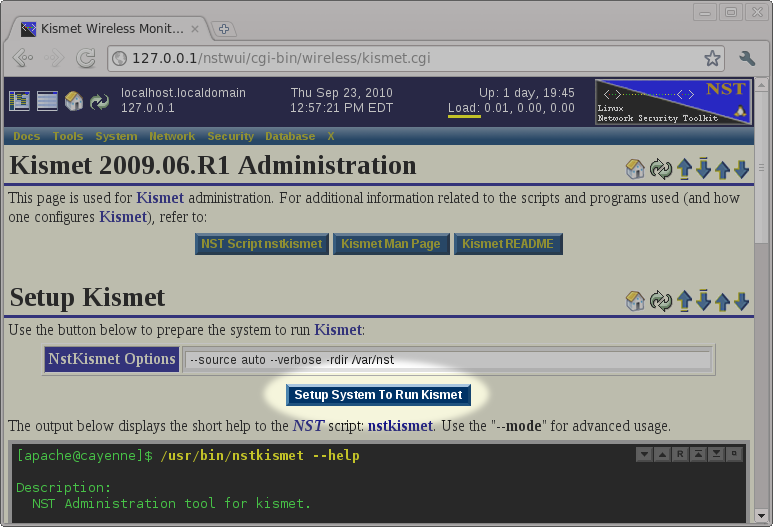
The '''NST''' ships with the necessary tools to setup and configure the system to run the ''' | The '''NST''' ships with the necessary tools to setup and configure the system to run the '''kismet''' service. However, you must prepare and configure your system before you will be able to run the '''kismet''' service. The '''nstkismet''' script is used to prepare the system and you can run it simply by pressing the ''Setup System To Run Kismet'' button found on the ''Kismet Administration'' page. The default options shown in the image below should be sufficient for most systems. | ||
[[File:kismet-setup.png|center|frame|Setting up the NST system to run kismet using the NST WUI]] | [[File:kismet-setup.png|center|frame|Setting up the NST system to run kismet using the NST WUI]] | ||
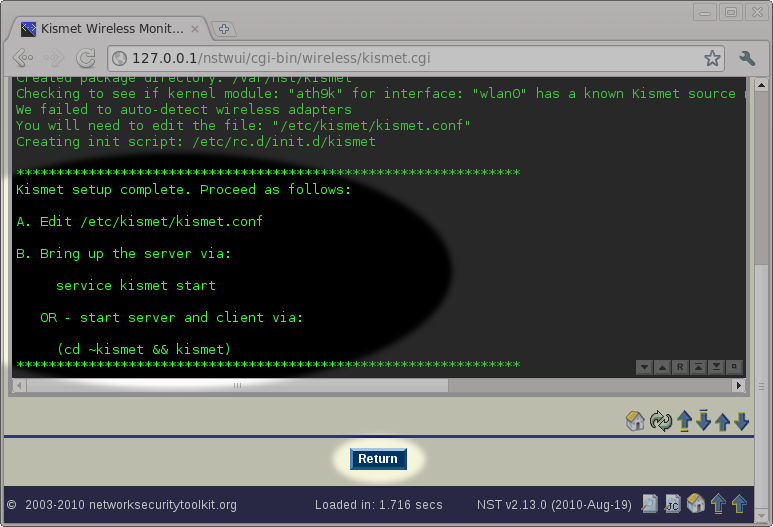
After pressing the ''Setup System To Run Kismet'' button, you will be taken to a page showing the results of running the '''nstkismet''' script. The output will indicate whether your wireless card was auto-detected or not. It will also tell you that you should review/edit the ''/etc/kismet/ | After pressing the ''Setup System To Run Kismet'' button, you will be taken to a page showing the results of running the '''nstkismet''' script. The output will indicate whether your wireless card was auto-detected or not. It will also tell you that you should review/edit the ''/etc/kismet/kismet.conf'' file and then start the ''kismet'' service. We will do these two steps using the '''NST WUI'''. For now, we simply need to press the ''Return'' button near the bottom of the page. | ||
[[File:kismet-setup-complete.png|center|frame|Results from setting up kismet using the NST WUI]] | [[File:kismet-setup-complete.png|center|frame|Results from setting up kismet using the NST WUI]] | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
[[File:kismet-edit-start.png|center|frame|Editing the kismet configuration file using the NST WUI]] | [[File:kismet-edit-start.png|center|frame|Editing the kismet configuration file using the NST WUI]] | ||
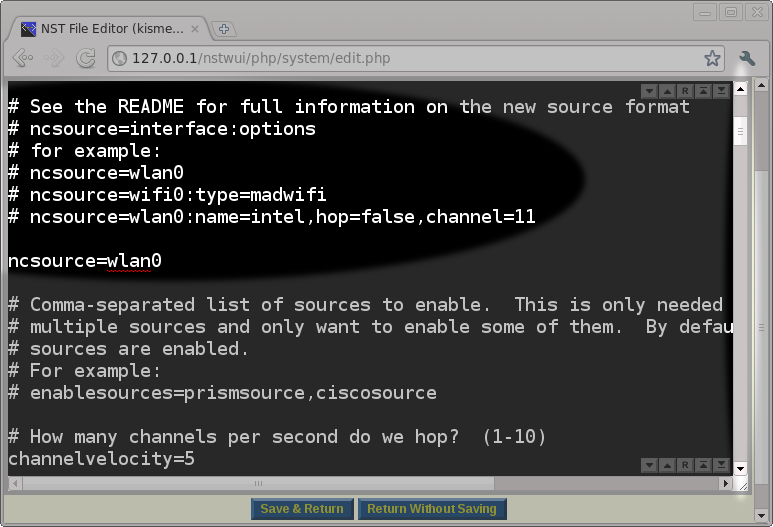
There are a lot of options that can be set in the ''/etc/kismet/kismet.conf'' file. The default values for most of the settings will work. However, you must set the ''ncsource'' parameter correctly for your system. After reviewing the Kismet README file (Use the: ''Kismet README'' button), we determined that we would start out by setting the ''ncsource'' parameter to our wireless interface ''wlan0'' and omit all of the optional ''ncsource'' settings as a starting point. We can always come back later if we decide to tweak the ''ncsource'' options shown in the Kismet README. | |||
[[File:kismet-edit-source.png|center|frame|Editing the kismet | [[File:kismet-edit-source.png|center|frame|Editing the kismet ncsource interface(s) using the NST WUI]] | ||
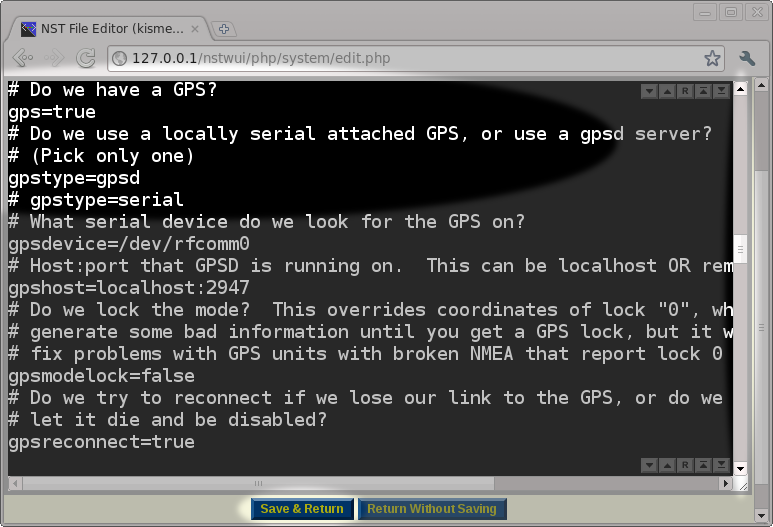
After setting the ''ncsource'' parameter in the configuration file, we scrolled down to the GPS area to make sure that the GPS was enabled and configured to use the '''gpsd''' service running on the ''localhost'' (127.0.0.1). We chose this GPS configuration because we have already setup the '''NST''' system to run the '''gpsd''' service by following the directions in: "[[HowTo Setup The NST System With A GPS (gpsd)]]". After verifying the GPS settings as being correct, we will press the ''Save & Return'' button to save our edits and return to the ''Kismet Administration'' page. | |||
[[File:kismet-edit-gps.png|center|frame|Editing the kismet GPS configuration using the NST WUI]] | [[File:kismet-edit-gps.png|center|frame|Editing the kismet GPS configuration using the NST WUI]] | ||
Revision as of 15:19, 13 October 2010
Kismet Prerequisites
Supported Wireless Card(s)
As a general rule of thumb, most WIFI adapters based on a Aetheros or Intel chip set should work "out of the box" when setting up Kismet on a NST system. To get an idea of the chip set used by your WIFI adapter, you can use the lspci command. The example output shown below is from running lspci on a ASUS Eeee PC and tells us that the system is using a Aetheros based chip set:
[root@cayenne trunk]# lspci ... Removed output for non-WIFI related hardware ... 02:00.0 Network controller: Atheros Communications Inc. AR9285 Wireless Network Adapter (PCI-Express) (rev 01) [root@cayenne trunk]#
Kismet requires one or more WIFI adapters. The lspci command is useful at displaying what WIFI hardware is present on your system. However, the lspci output does not tell you whether the necessary drivers for the hardware are installed on the system. The iwconfig command will tell you what WIFI adapters are supported by the system. For example, the following shows that my system has one WIFI adapter (wlan0):
[root@cayenne trunk]# iwconfig
lo no wireless extensions.
eth0 no wireless extensions.
wlan0 IEEE 802.11bgn ESSID:"WRT610N-SHOP0"
Mode:Managed Frequency:2.437 GHz Access Point: 68:7F:74:03:3F:00
Bit Rate=65 Mb/s Tx-Power=20 dBm
Retry long limit:7 RTS thr:off Fragment thr:off
Encryption key:off
Power Management:off
Link Quality=50/70 Signal level=-60 dBm
Rx invalid nwid:0 Rx invalid crypt:0 Rx invalid frag:0
Tx excessive retries:0 Invalid misc:0 Missed beacon:0
[root@cayenne trunk]#
If your WIFI adapter is not recognized by the system, you may want to refer the Kismet site for more information and links. You might find information on how to download and install the necessary drivers for your your hardware.
GPS Device and gpsd Service
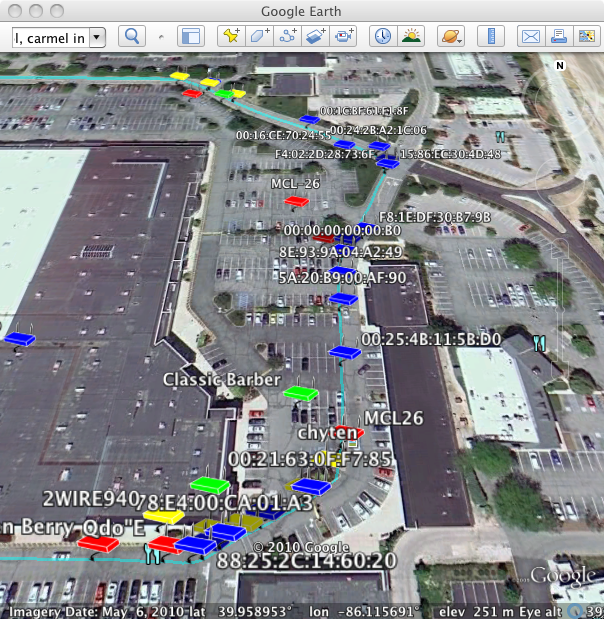
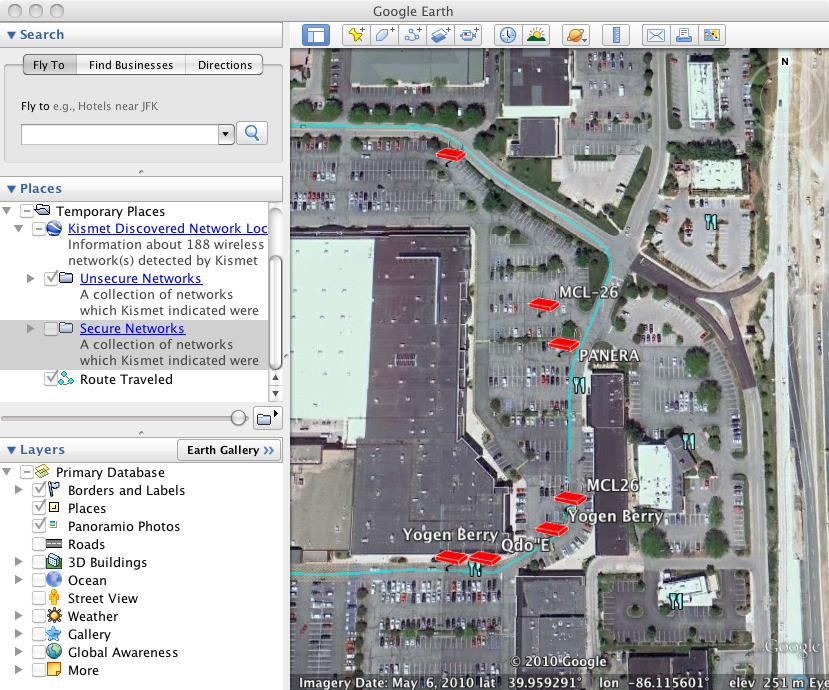
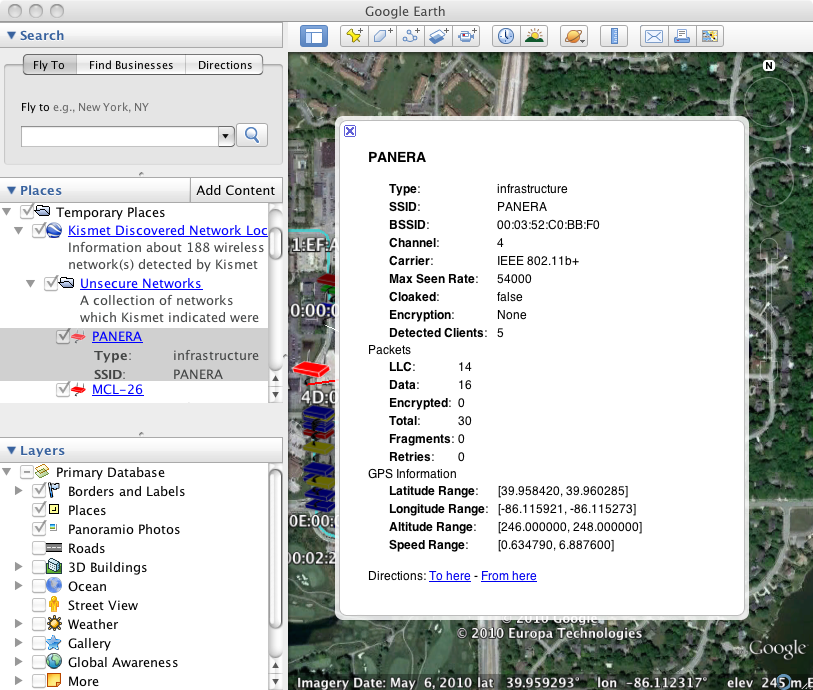
If you would like to be able to display the information collected by Kismet in Google Earth, you will need to connect a compatible GPS to your NST system and run the gpsd service. Refer to: "HowTo Setup The NST System With A GPS (gpsd)" for details on connecting a GPS to your NST system.
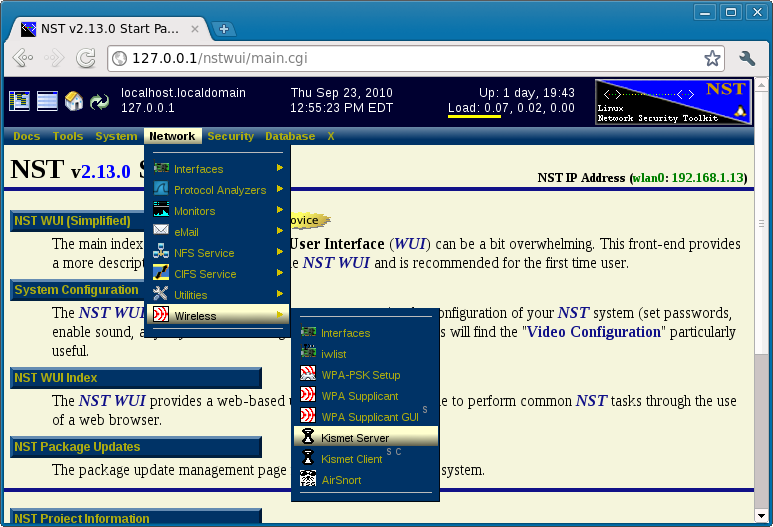
Locating the Kismet NST WUI Page
The following shows how you locate the Kismet server administrative page using the NST WUI:
Kismet Setup and Configuration
The NST ships with the necessary tools to setup and configure the system to run the kismet service. However, you must prepare and configure your system before you will be able to run the kismet service. The nstkismet script is used to prepare the system and you can run it simply by pressing the Setup System To Run Kismet button found on the Kismet Administration page. The default options shown in the image below should be sufficient for most systems.
After pressing the Setup System To Run Kismet button, you will be taken to a page showing the results of running the nstkismet script. The output will indicate whether your wireless card was auto-detected or not. It will also tell you that you should review/edit the /etc/kismet/kismet.conf file and then start the kismet service. We will do these two steps using the NST WUI. For now, we simply need to press the Return button near the bottom of the page.
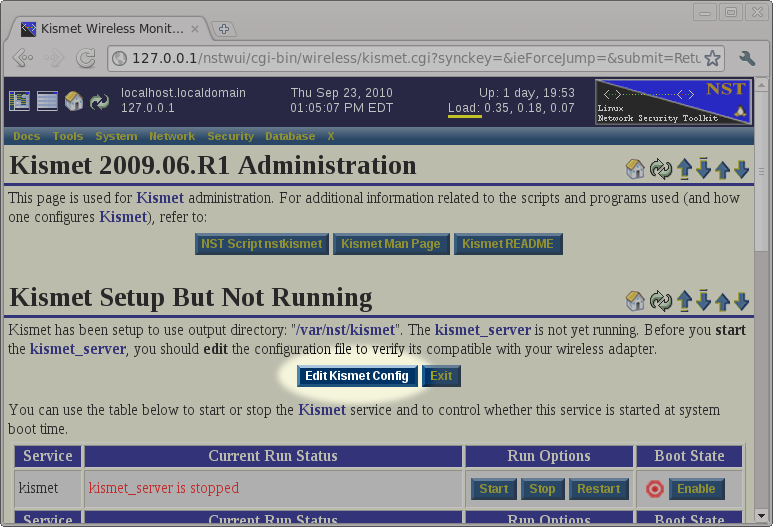
After returning to the Kismet Administration page, we will set that the system has been setup to run the kismet service, but that the service is not currently running. Before starting the service, we will use the Edit Kismet Config button to review and possibly change the default configuration.
***Note: If you are not familiar with Kismet, you should use the Kismet README and Kismet Man Page buttons to read up on using Kismet before continuing.
There are a lot of options that can be set in the /etc/kismet/kismet.conf file. The default values for most of the settings will work. However, you must set the ncsource parameter correctly for your system. After reviewing the Kismet README file (Use the: Kismet README button), we determined that we would start out by setting the ncsource parameter to our wireless interface wlan0 and omit all of the optional ncsource settings as a starting point. We can always come back later if we decide to tweak the ncsource options shown in the Kismet README.
After setting the ncsource parameter in the configuration file, we scrolled down to the GPS area to make sure that the GPS was enabled and configured to use the gpsd service running on the localhost (127.0.0.1). We chose this GPS configuration because we have already setup the NST system to run the gpsd service by following the directions in: "HowTo Setup The NST System With A GPS (gpsd)". After verifying the GPS settings as being correct, we will press the Save & Return button to save our edits and return to the Kismet Administration page.
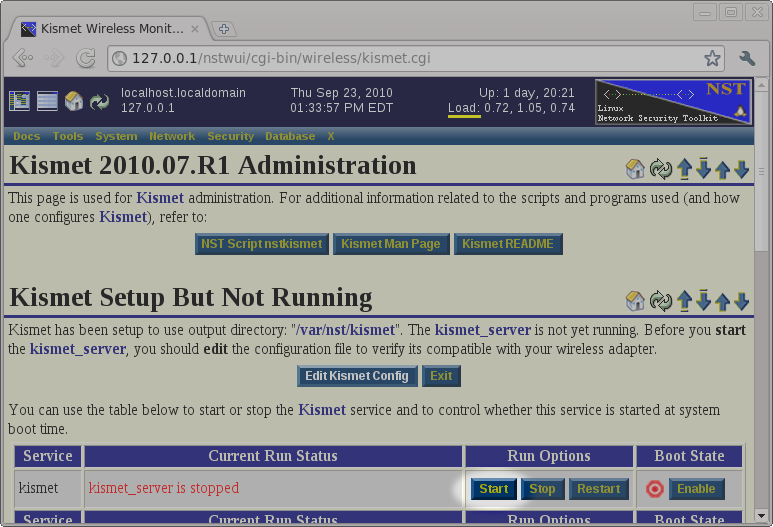
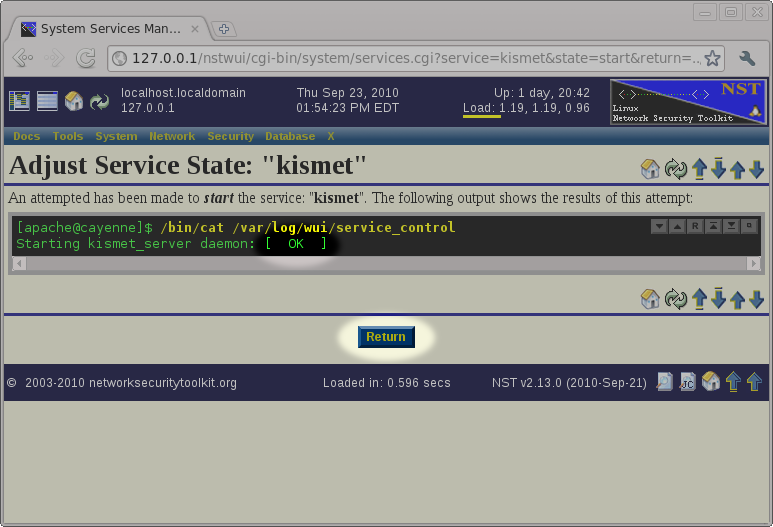
Starting The Kismet Service
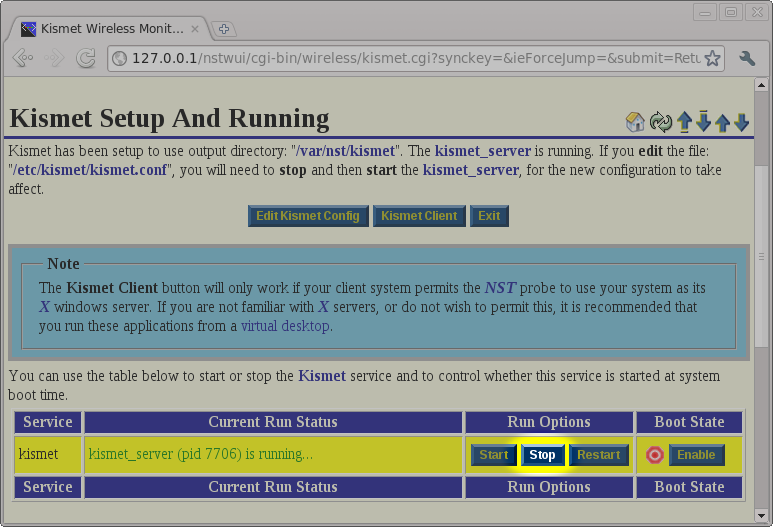
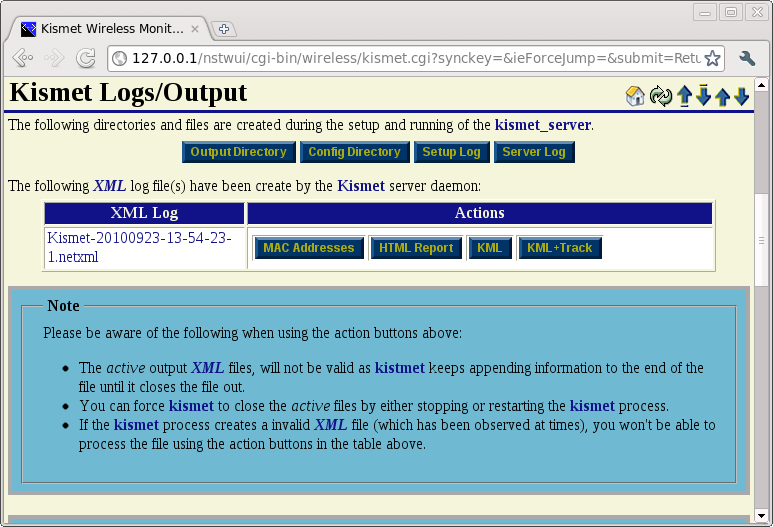
Kismet Results
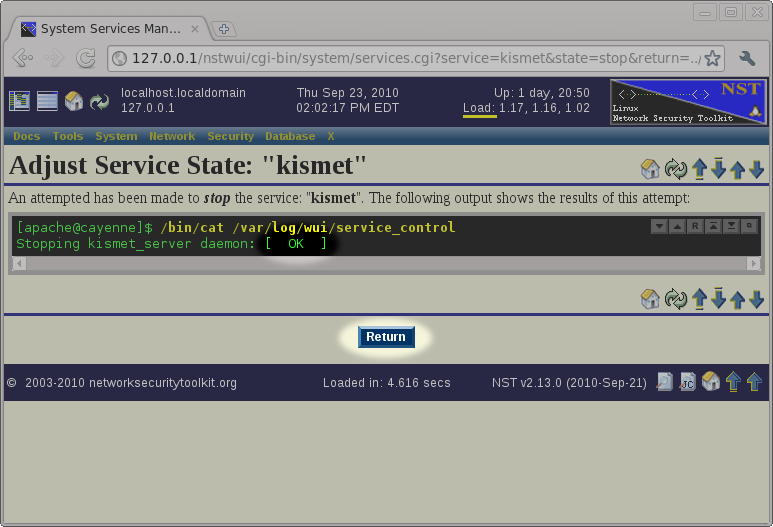
Stopping The Kismet Service
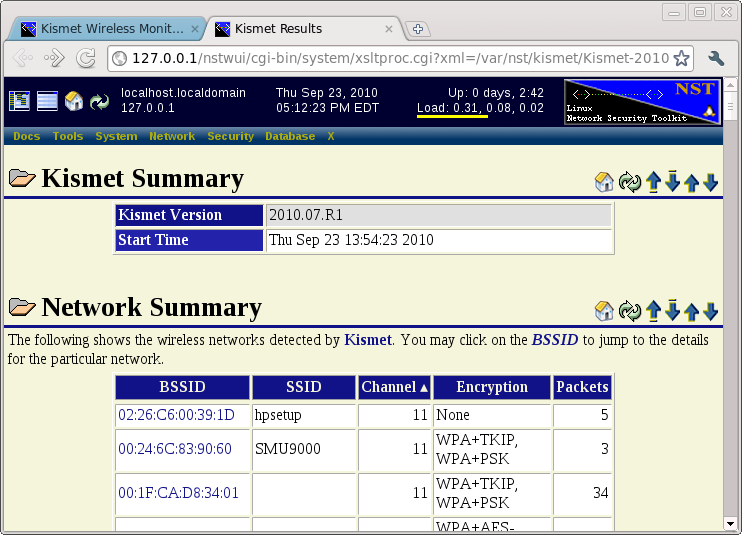
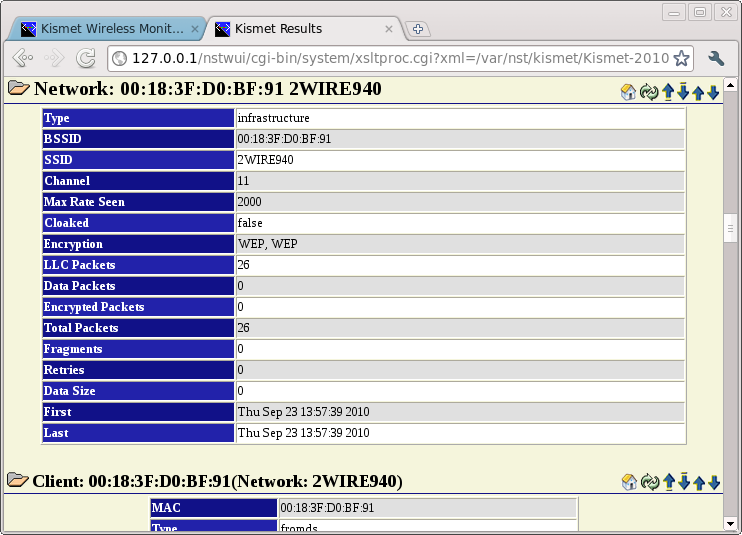
The Kismet Results Table
MAC Addresses
00:02:2D:28:73:6F 00:8A:29:BF:7D:10 00:02:2D:BF:7D:10 D0:B0:3C:BF:7D:10 00:02:2D:BF:7D:10 00:66:00:00:00:00 00:02:2D:BF:7D:10 00:02:2D:BF:7D:10 00:02:2D:BF:7D:10 0B:1C:6B:3A:38:11 00:02:2D:BF:7D:10 00:02:2D:BF:7D:10 00:02:2D:BF:7D:10 00:02:2D:2A:60:6F 98:02:2D:28:73:6F 00:02:2D:BF:7D:10 32:C6:2C:BF:32:9D 00:02:2D:BF:7D:10
HTML Table
KMZ (Google Earth)