HowTo Geolocate ntop Data: Difference between revisions
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
Use the ''''ntop Hosts - KML'''' button to generate on demand '''Geolocated ntop Hosts''' rendered on a '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keyhole_Markup_Language KML]''' '''Earth Browser''' such as '''[http://earth.google.com Google Earth]'''. One can override the '''Map Annotation''' if necessary. Generating a '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keyhole_Markup_Language KML]''' document can take some time depending on the number of hosts to geolocate. We have observed that to geolocate 1000 hosts, it takes roughly between 40 and 50 seconds to complete. | Use the ''''ntop Hosts - KML'''' button to generate on demand '''Geolocated ntop Hosts''' rendered on a '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keyhole_Markup_Language KML]''' '''Earth Browser''' such as '''[http://earth.google.com Google Earth]'''. One can override the '''Map Annotation''' if necessary. Generating a '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keyhole_Markup_Language KML]''' document can take some time depending on the number of hosts to geolocate. We have observed that to geolocate 1000 hosts, it takes roughly between 40 and 50 seconds to complete. | ||
Each host marker contains a | Each host marker contains a ''''Host Description'''' balloon depicting selective '''[http://www.ntop.org ntop]''' network statistics information and linkage back to one or more NST WUI ''''IP Tools'''' pages for additional network processing using the host's IP Address. | ||
{|cellpadding="10" | {|cellpadding="10" | ||
| Line 97: | Line 97: | ||
|} | |} | ||
When using '''[http://earth.google.com Google Earth]''', one can also view the | When using '''[http://earth.google.com Google Earth]''', one can also view the ''''Document Description'''' balloon by clicking on the generated '''[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keyhole_Markup_Language KML]''' '''ntop Hosts''' label found under '''Temporary Places''' within the sidebar on the left-hand side. | ||
=== '''IP Geolocation Adjustments''' === | === '''IP Geolocation Adjustments''' === | ||
Revision as of 11:49, 21 September 2010
Overview
This HowTo explains the procedure for setting up an ntop session and producing on demand host geolocations rendered on either a Mercator World Map projection or on a KML Earth Browser such as Google Earth, Google Maps or Marble.
One of the goals of the NST WUI is to provide a web-based front-end to numerous open source network security applications. Trying to build out a web-based interface that has a common look-and-feel across the vast spectrum of applications is a daunting task. Once an NST WUI interface is mastered, it will become a routine task for the network security administrator to use it across different NST systems and network infrastructure environments.
Before diving into producing ntop Hosts Geolocations, one needs to understand best practices on how to setup an ntop session as a Host data source collector. This first involves getting ntop up and running using its NST WUI management interface and then secondly controlling how much data ntop is configured to collect using ntop administrative settings.
ntop Setup Management
This section describes how to setup an ntop session using the NST WUI. The screen shot below shows one how to locate the ntop Management page using the NST menu bar.
Network Interface(s)
The input and selection fields provided by the NST WUI management interface will be explained so that one can quickly start up ntop. One or more network interfaces can be selected (i.e., click on an associated check box) to be monitored by the ntop application. One can click on a NIC adapter icon to examine detailed counter data and interface controls associated with a network adapter. This feature can be particularly useful if one wants to know if traffic is currently occurring on a network interface prior to bring up the ntop session. For best results when geolocating Hosts using ntop data, select a network interface to monitor that has a public IP Address presence (e.g., Network Tap or SPAN port associated with the dirty side of a corporate firewall or a web server farm located in a DMZ).
A network interface does not have to have a binding IP Address (i.e., stealth interface) and can also be in the Down state. The NST WUI will bring all selected network interfaces from the Down state to the Up state prior to starting the ntop session.
HTTP / HTTPS Access
Access to the ntop user interface can be configured to use either the HTTP and/or the HTTPS protocol. This is done by setting a non-zero Access Port value for the associated protocol. An access port value of Zero (0) will disable the use of the protocol. Typically, an access port value of 3000 is used for HTTP and an access port value of 3001 is used for HTTPS.
Setup ntop Options
The script: "setup_ntop" is used to support the NST WUI by creating a runtime execution environment for ntop and starting up the ntop daemon. The Setup ntop Options field allows one to add setup and runtime options associated with the script: "setup_ntop". Normally, other than specifying the runtime directory: "--rdir /var/nst", this field does not need to be altered. For detailed additional setup ntop options, expand the Setup ntop Options section on this NST WUI page.
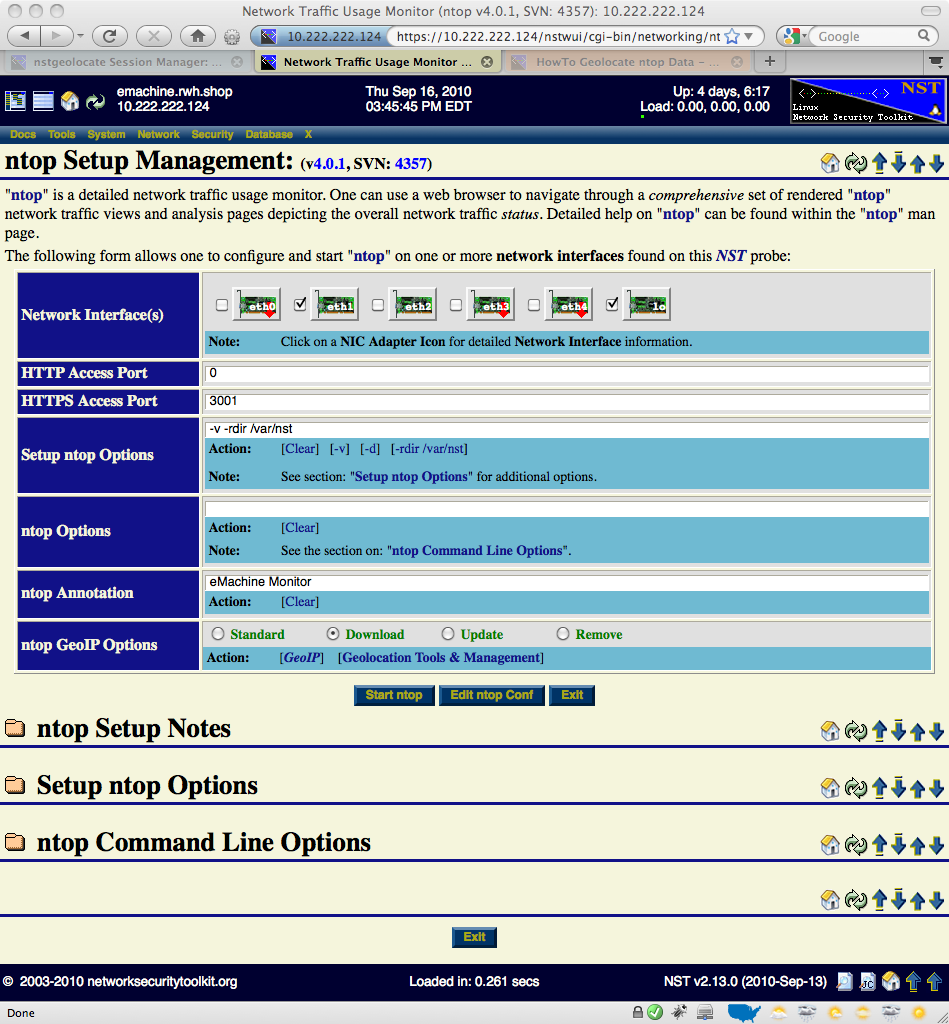
ntop Options
The ntop Options field is used to specific additional ntop parameters that are not provided automatically by the NST WUI ntop Setup Management interface (e.g., Add an option so that Idle hosts are not purged from memory and set the Refresh page time in seconds to 1 min: "--sticky-hosts --refresh-time 60"). For detailed additional ntop options, expand the ntop Command Line Options section on this NST WUI page.
ntop Annotation
Enter a Map Title or a short (i.e., 22 characters or less) Annotation to describe this ntop session (e.g., Wiki Web Site Traffic). This text will appear on rendered geolocation map projections or within a geolocation KML document description balloon.
ntop GeoIP Options
In order for both the ntop application and NST to perform Host geolocations, a database must exist to look up the earth coordinate (i.e., latitude, longitude) for a given IPv4 Address. The GeoIP database from MaxMind is used by ntop. There are two approaches for downloading the GeoIP database. One can simply choose the Download radio button or follow the method for downloading the GeoIP database found on the Geolocation Tools & Management page. Use the Standard radio button to disable downloading the GeoIP database. Use the Update radio button to refresh an existing GeoIP database. Lastly, use the Remove radio button to delete the entire GeoIP database from the NST system.
View / Edit ntop Configuration File
One can also use the NST File Editor to view or make permanent changes to the ntop configuration file: "/etc/ntop.conf". Click on the 'Edit ntop Conf' button to perform this task.
Starting Up An ntop Session
Once you are satisfied with your ntop configuration options, commence an ntop session by clicking on the 'Start ntop' button. An intermediate page displaying the results of starting up the ntop session will be presented next as shown below. Click on the 'Return' button to continue with the setup sequence.
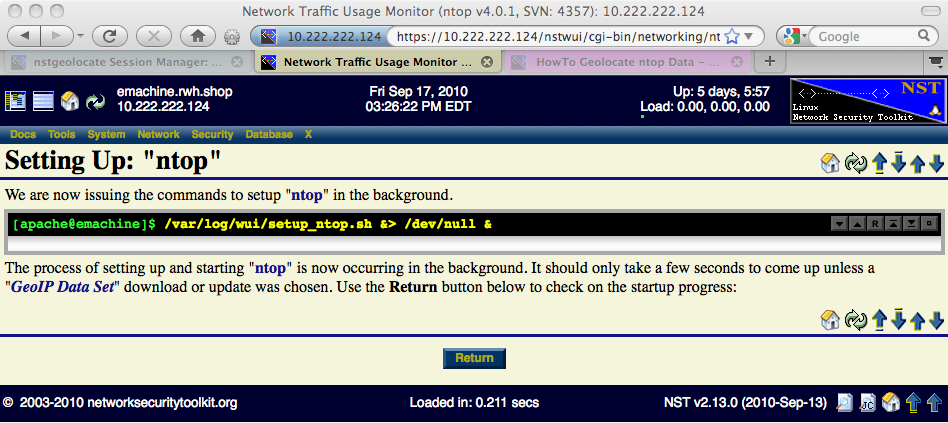
ntop Setup In Progress
The ntop session setup time will take longer if the GeoIP database needs to downloaded or updated. You can monitor the progression of the setup using the 'Monitor ntop Setup Log' button or periodically click on the 'Refresh' button to see if the session setup has completed.
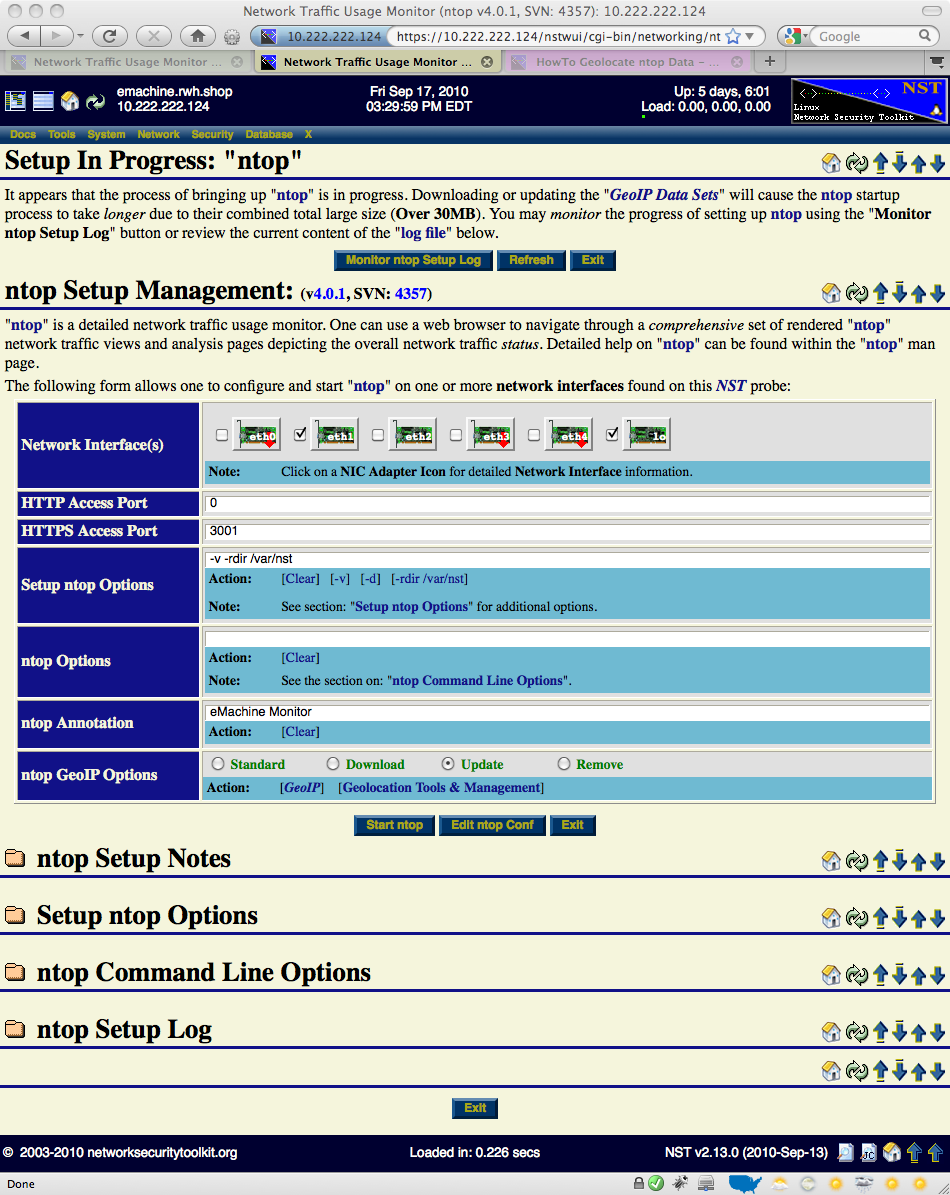
ntop Runtime Management
Once an ntop session is up and running, one can enter the ntop user interface, manage the ntop daemon or produce on demand host geolocations.
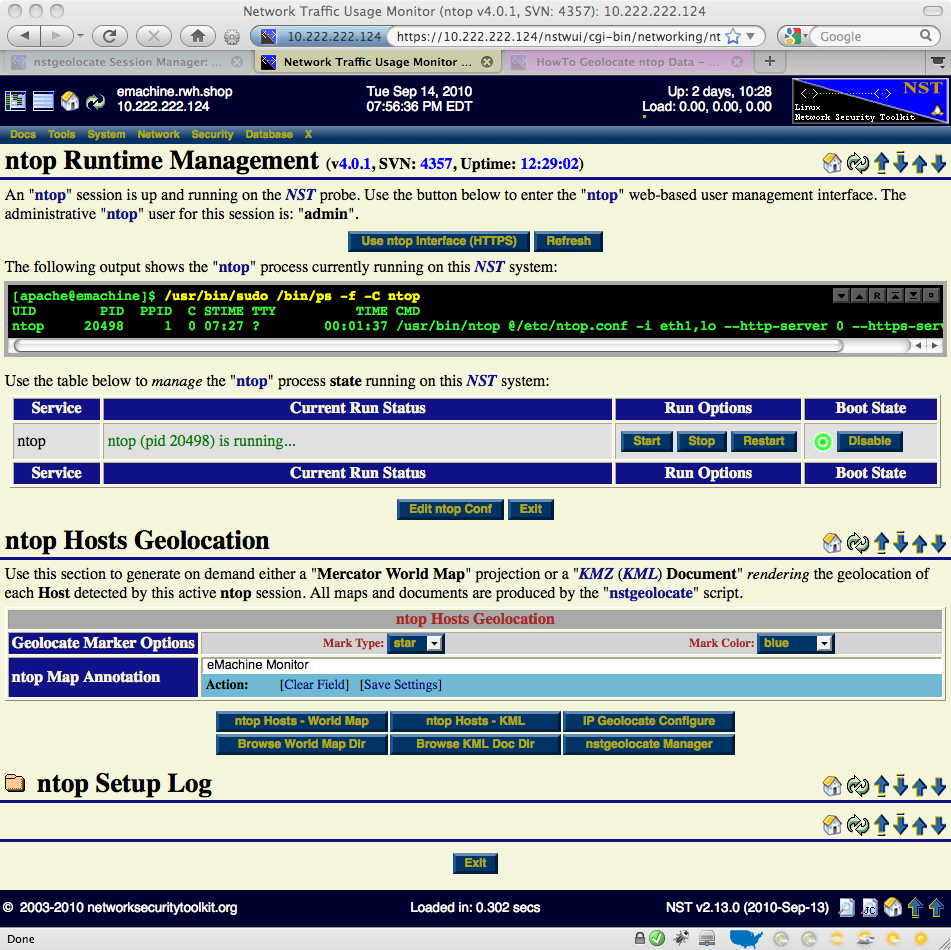
Geolocate ntop Hosts
This section will show how to produce on demand host geolocations rendered on either a Mercator World Map projection or on a KML Earth Browser such as Google Earth, Google Maps or Marble. The NST script: nstgeolocate is used to support the NST WUI when generating host geolocations.
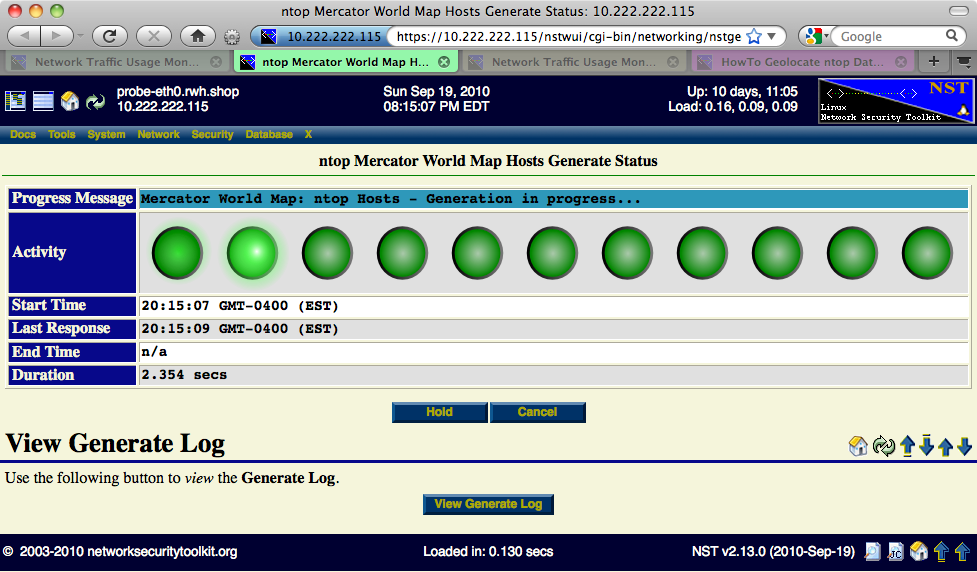
Mercator World Map
Use the 'ntop Hosts - World Map' button to generate on demand Geolocated ntop Hosts rendered on a Mercator World Map projection. You can customize the host geolocation marker type and color. One can also override the Map Annotation if necessary. The following Progress Generation page is displayed while the ntop Hosts are in the process of being geolocated and rendered on the Mercator World Map projection.
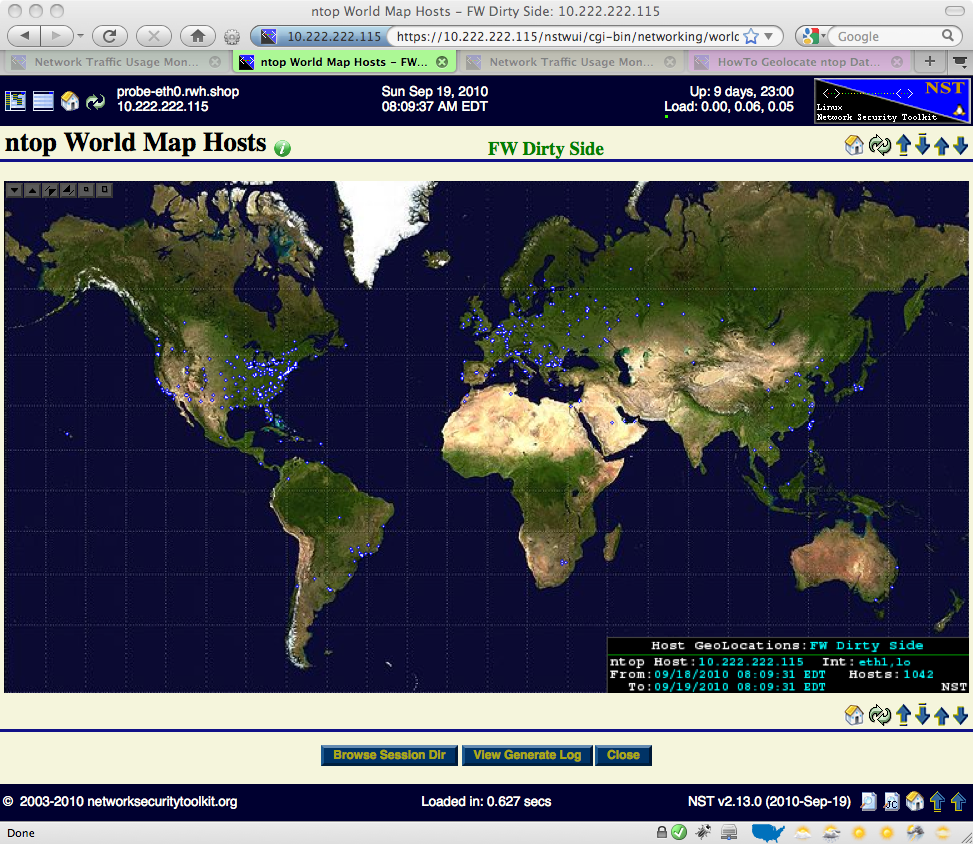
Once the process of geolocating and rendering hosts on the Mercator World Map has completed, the resultant map will be shown in a new tab or browser window. The ntop World Map Hosts image shown below was produced using marker type: "star" with marker color: "blue".
Use the Image Control Button Grid located in the upper left-hand corner of the map to both position and resize the map projection. Hover your mouse pointer over the information icon to reveal a detailed description associated with the Geolocated ntop Hosts. The map below was zoomed in and also is showing the information tooltip balloon.
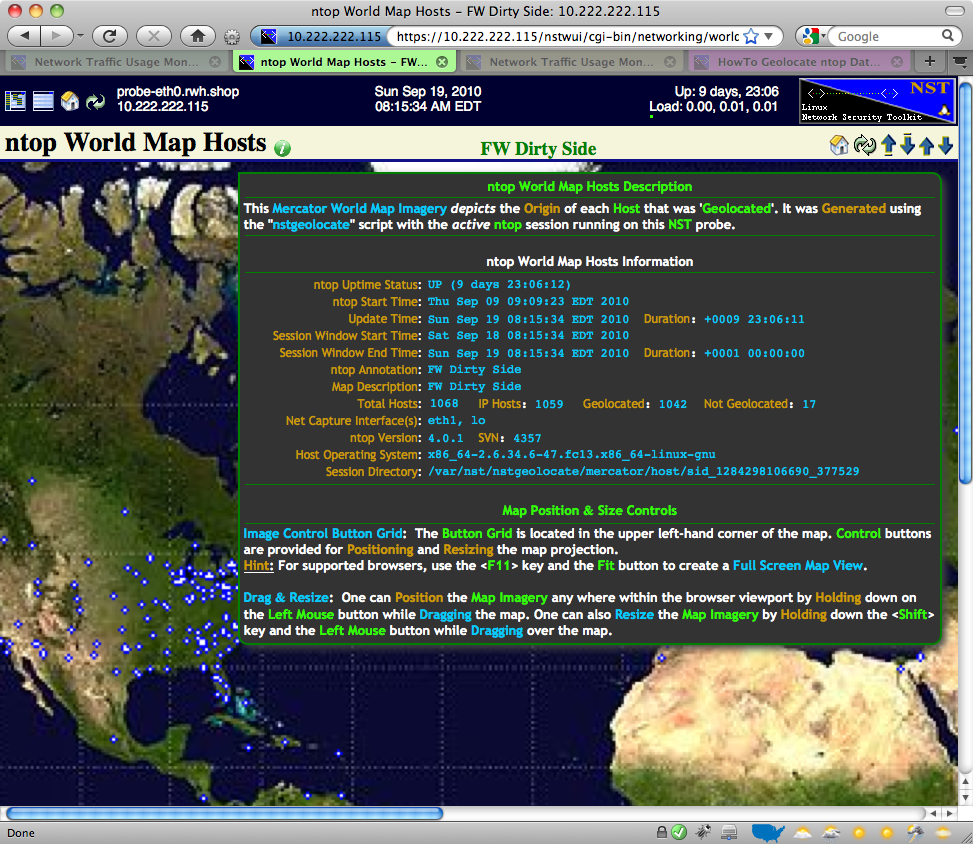
World Map: Image Control Button Grid
The caption below describes each button associated with the World Map Image Control Grid. For supported browsers, try creating a full screen map view by using a combination of the 'F11' function key and the 'Fit To Browser Window Viewport' button.
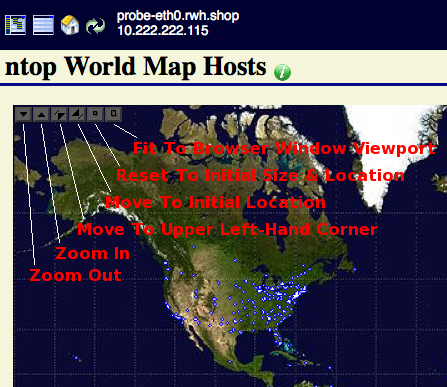
World Map: Drag & Resize
Try resizing and positioning the Mercator World Map using a combination of your Left Mouse button and the Shift key while dragging the mouse. See the description in the 'ntop Mercator World Map Hosts - Zoomed In with Information Tooltip Balloon' screen shot above. The Drag & Resize functionality uses a JavaScript library created by Walter Zorn. Documentation for the library can be view here: DHTML API, Drag & Drop for Images and Layers
KML Document
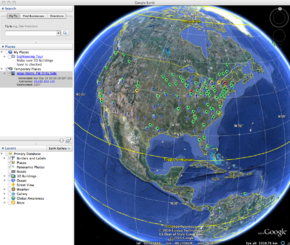
Use the 'ntop Hosts - KML' button to generate on demand Geolocated ntop Hosts rendered on a KML Earth Browser such as Google Earth. One can override the Map Annotation if necessary. Generating a KML document can take some time depending on the number of hosts to geolocate. We have observed that to geolocate 1000 hosts, it takes roughly between 40 and 50 seconds to complete.
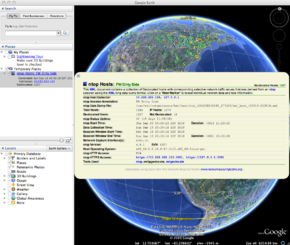
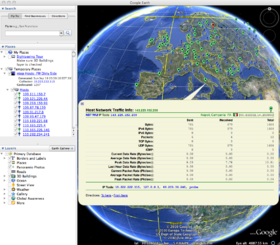
Each host marker contains a 'Host Description' balloon depicting selective ntop network statistics information and linkage back to one or more NST WUI 'IP Tools' pages for additional network processing using the host's IP Address.
 |
 |
 |
When using Google Earth, one can also view the 'Document Description' balloon by clicking on the generated KML ntop Hosts label found under Temporary Places within the sidebar on the left-hand side.
IP Geolocation Adjustments
Use the ' IP Geolocate Configure' button to manage the global geolocation policy for this NST system. This allows one to make latitude and longitude coordinate adjustments, configure private IPv4 Address/Network coordinate locations and select a Geolocation database source. In addition, one can also download and manage the MaxMind "GeoIP Country Edition", the enhanced "GeoIP Lite City Edition" and the "GeoIP AS Number Edition" data sets.